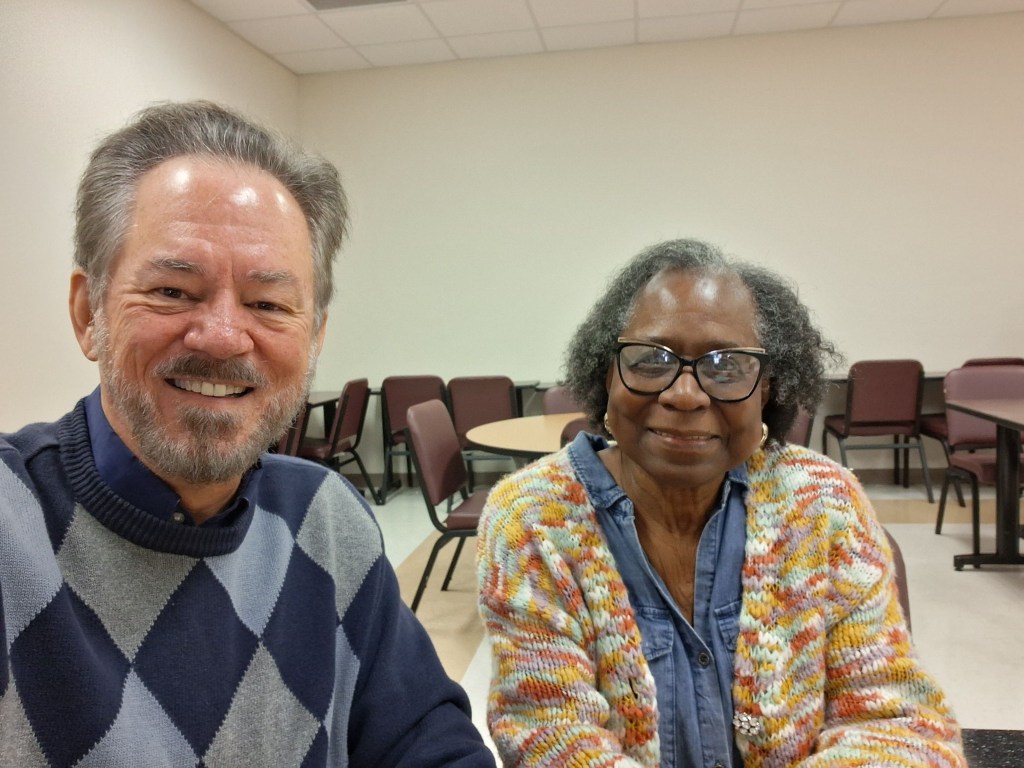
Breaking Barriers: The story of the first Black students at a Mississippi Baptist college
Copyright by Robert C. Rogers

On March 5, 1965, the trustees of William Carey College (now William Carey University) voted to comply with the Civil Rights Act of 1964, promising not to discriminate based on “race, color, or national origin.” Thus, the Baptist college became the first Southern Baptist institution in Mississippi to racially integrate.
Carey’s president, Dr. J. Ralph Noonkester, contacted the principal of Hattiesburg’s Rowan High School to recruit the first Black students. The principal spoke to the parents of Linda Williams and Vermester Jackson, two honors graduates, and their parents approached each young lady about the possibility of becoming the first Black students at Carey.
Neither Linda nor Vermester had considered the possibility. Although her own grandmother had been a housekeeper at the college for years, it never occurred to Linda that she would be a student there. Linda responded to her parents, “We go where?” She had planned to go to Mississippi Valley State, a historically Black college where she had friends.
Vermester already had a scholarship to Southern Illinois University in Carbondale, Illinois, when her parents approached her about going to college at Carey. “My mother said, there are lots of kids who can’t go anywhere with a scholarship like you can,” implying that she could break the color barrier for other students if she went to Carey. “We decided to do it.”
“We had no idea what danger we were in,” said Linda. Unknown to either girl, the night before their first day at school, the Ku Klux Klan burned a cross on the lawn of President Noonkester. That night, Black residents in their neighborhood slept with shotguns by their beds, something Vermester’s parents only told her later. Linda said, “My Dad was apprehensive; he feared a firebombing of our yard.”
Linda and Vermester lived near the campus, on opposite ends of Royal Street. Linda said, “I lived on the west end, and she lived on the east end of the street, so we met up at Tuscan Avenue and we both walked to school.” Vermester remembered smelling something, but didn’t know about the cross-burning, as it had been cleaned up. As they walked up to Tatum Court on the Carey campus, Linda asked her, “Girl, are you scared?” Right then, they saw a Black maid cleaning the stairs, who said, “We’re watching out for y’all.” The maid was right. In fact, Linda says, “We had five young Christian women [students] who met us on campus and led us around to show us our buildings. It was very comforting to know we didn’t have to do it alone. That made the transition pretty easy.” Vermester added, “That first day, every time I turned around, I could see Dr. Noonkester. He would stop and ask how things were going.”
At the same time, their friend Gwendolyn Elaine Armstrong was one of two Black students integrating Hattiesburg’s other college, Southern Miss. Armstrong and the other Black students at Southern Miss had to have protection from the National Guard, and she told Vermester that students were spitting on them. “But we didn’t have any group that showed hatred or disapproval,” said Linda. “I remember some heckling,” she added, but compared to their high school classmates’ experience at Southern Miss, they would say to each other, “Girl, we’re blessed.”
Vermester was a math and English major, and Linda was a business major, so they only had one or two classes together, including an English composition class. When they walked into that classroom, a young man got up and left. Years later, Linda met the same man when he came to pay his bill at Mississippi Power Company where she was working. Recognizing her, he apologized. Another memory both Linda and Vermester had of that class together was how their teacher pronounced the word “Negro” in a short story she was reading, so it sounded more like the N-word.
Despite having few classes together, both girls studied hard and were encouraged by the faculty to join organizations and get involved. Their greatest encouragement, however, came from their families and the Black community. Their parents made sacrifices for them, such as relieving them of chores, so they could study. Neighbors would ask, “Do you need any help?” The second semester some Black students transferred in from Prentiss Institute and Mississippi Valley State, making at least five Black students on campus. The following year, Black enrollment increased a good bit, and some of their classmates from Rowan High School came.
Their junior year, Linda transferred to Mississippi Valley State “to experience dorm life,” but she decided she wasn’t going to let Vermester walk across the stage at graduation by herself, so she returned to Carey for graduation. By the time they graduated in 1969, there were photographs of 76 Black students in the Carey yearbook. They were from all of Mississippi, but most were from Hattiesburg.
After college, Linda and Vermester went separate ways. Vermester married Mr. Bester and taught math in the Hattiesburg Public Schools, retiring from Hattiesburg High School. She never talked about being one of the first Black students at William Carey University. She said, “For the longest time, it didn’t occur to me what Linda and I had done.” Other people talked about it, though. “I’ve had people come up to me and say, ‘If it hadn’t been for you and Linda, I wouldn’t have been able to go to school.’ It warms my heart.” She is proud to say that her grandson, Cory Bester, graduated from Carey.
Linda eventually moved out of state, living many years in Minnesota before retiring in Pensacola, Florida, where she resides today. “I’ve had men and women tell us, if you had not done this, we would not have gotten our degrees. I had a young lady I babysat, who later got her doctorate there. I have a niece and a nephew who went to Carey,” says Linda. Two scholarships to William Carey University have been established in their names, one a partial scholarship and the other a full scholarship.
However, Linda did not receive her own diploma. A mix-up over her transfer to Valley State and back to Carey somehow caused her to miss 3 hours credit that she thought she had when she walked across the graduation stage in 1969. Back then, they would mail the real diploma after graduation, but she never received it. In 2024, she and her son were on the Carey campus and met the current president, Dr. Ben Burnett. When they explained what happened, he said, “We’re going to fix that.” On May 10, 2024, Linda Williams was the last person to walk across the stage of the graduation ceremony at William Carey University, and she received her diploma at last. “They gave me two standing ovations. It was like I was graduating all over again! It was so surreal. Dr. Noonkester’s son, Myron, had the honor of giving me the diploma his Dad would have given me,” said Linda. Linda thought of her grandmother, who was a housekeeper at the college when it was known as Mississippi Woman’s College. “She would have loved to have seen that happen to me.”
Vermester says, “What I treasure most is that William Carey College lived up to the Christian spirit. Somehow, they managed to make it happen, in a way that benefitted us and our community.”

SOURCES: Linda Williams, telephone interview by author, February 7, 2026; Vermester Jackson Bester, in-person interview by author, February 4, 2026; Robert C. Rogers, Mississippi Baptists: A History of Southern Baptists in the Magnolia State (Mississippi Baptist Convention Board, 2025), 224-225.
New devotional through Psalms & Proverbs in a year

Psalms & Proverbs Weekday Devotionals is my new e-Book with a daily reading plan to read through Psalms and Proverbs weekdays, Monday through Friday, in a year, accompanied by short devotional thoughts to edify your reading. Readings are arranged by weeks and days, not tied to months of the year, so you may begin at any time of the year.
Here is a sample, showing the first reading:
Week 1, Day 1
Read Psalm 1
Psalms 1:1 literally says the one who is blessed does not “walk,” or “stand,” or “sit” with the wicked. There is a progression here of lingering longer and longer with evil. That’s usually how we fall into sin– gradually. I know I have fallen into sin that way. The solution is in verse 2: Meditate on God’s Word both day and night! I pray these daily psalms and proverbs will protect you from sin and guide you with wisdom.
Read Proverbs 1:1-6
Proverbs 1:5 says a wise man will listen and increase his learning. James 1:19 says, “Everyone must be quick to hear, slow to speak…” An excellent resolution is to become a better listener in the New Year.
The e-Book is 164 pages. Buy it for just $2.99 on Amazon here.
Best biographies I read in 2025
If you know me, you know that I nerd out on history. In 2025, I read a lot of biographies. These were particularly interesting to me:

*Confessions of St. Augustine. The spiritual and psychological autobiography of one of the greatest theologians in history. What more can I say? Read it!

*William Carey, by S. Pearce Carey. A masterful story of the father of modern missions by his great-grandson. Inspiring beyond measure. Thanks to Dr. Bennie Crockett for recommending it.

*The Revolutionary, Samuel Adams, by Stacy Schiff. With our nation’s 250th anniversary coming up, I wanted to read up on that era. Schiff shows how Samuel Adams was perhaps the greatest instigator behind the revolution. Fascinating.

*Alexander Hamilton, by Ron Chernow. No wonder they made a Broadway play based on this book. The guy had more drama in his lifetime than some nations have in their entire history.

*The Pirates Lafitte, by William C. Davis. Entertaining and illuminating about the Gulf Coast culture and history in the early 1800s through the raucous lives of the pirates Jean and Pierre Lafitte. I really enjoyed this one.
As If Heaven Had Ordained It

“Not one word of all the good promises that the Lord had made to the house of Israel had failed; all came to pass.” – Joshua 21:45
When the Continental Congress gathered in Philadelphia in 1774 to unite against the British, they decided to open their proceedings in scripture and prayer. An Episcopalian minister named Jacob Duché was chosen. Before his prayer, rumors arrived that the British had attacked Boston. A frightened and receptive audience awaited as Duché read Psalms 35:1: “Contend, O LORD, with those who contend with me; fight against those who fight against me!” It was the assigned reading for the day in the Episcopal lectionary, but John Adams says members of the Continental Congress were stunned when they heard the words. Adams wrote, “It seemed as if Heaven had ordained that psalm to be read on that morning.” Have you had such an experience where the scripture seemed perfect for what you were going through at the time? I have several such scriptures marked in my Bible. Once when I was anxious about a situation at work, I read Psalm 34:4, “I sought the LORD, and he answered me and delivered me from all my fears.” That verse gave me sudden comfort. Eventually, everything worked out. Another verse that has helped me when facing a difficult decision is the promise of James 1:5, “If any of you lacks wisdom, let him ask God, who gives generously to all without reproach, and it will be given him.” Praying over that promise, God has given me direction time after time. Once when I was a hospital chaplain, I visited a patient writhing in pain, asking me to pray. As I was about to pray, two nurses entered and gave her tablets to take for pain, then left the room. Immediately I began to pray, and I sensed God telling me to quote Psalm 23, so I did. Even before I finished the psalm, she grew peaceful and still. I finished quoting the psalm, added a few more words asking God for healing, and then I looked up. The patient was resting. Her sister-in-law looked at me, eyes wide in amazement. I said, “That pain medicine hasn’t had time to work, has it?” The sister-in-law said, “No, but Psalm 23 did!” What scripture has given you guidance, comfort, or strength “as if Heaven had ordained” it?
Prayer
Lord, my heart is full of anxieties and desires, but your word is full of good promises and timely guidance. As I read scripture, show me how it applies to my life as if Heaven had ordained it for this day.
Book review: “Crusaders” by Dan Jones

Dan Jones. Crusaders: The Epic History of the Wars for the Holy Lands. Viking, 2019.
I have read several books on the Crusades, but this is the best I’ve read so far. Dan Jones has written numerous books on the Europeans in the Middle Ages, so this is his area of expertise. His work is thoroughly researched, but he also writes in an engaging style, opening most chapters with vignettes about colorful personalities, and he peppers the book with fascinating quotes and interesting details.
The title Crusaders (instead of “Crusades”) is deliberate, because, as Jones explains in his preface, he focuses on the personalities like Richard the Lionheart, telling stories of the combatants (mostly Christian, but he also gives coverage to prominent Muslim warriors, including a chapter on Saladin). Yet he tells the story in chronological order, which helps the reader to follow the facts.
With so much blood and horrendous violence, Jones could easily depict the Crusaders as pure evil, but as a good historian he leaves it to the reader to make moral judgments, even reminding the reader at times that as bad as the violence was, it was normal for all sides at that time in history. He simply tells the facts and quotes the sources that describe the characters, whether evil or holy, or, as many were, a mixture of both. The book truly helps the reader understand the reasons why the Crusades happened as they did by helping the reader understand life in the Middle Ages. Until I read this book, I didn’t fully understand why the Fourth Crusaders plundered Constantinople instead of invading Muslim territory, but now I understand the economic motivations of the Venetians.
The old adages about history repeating itself and not learning lessons from history are evident in these stories. One example is the defeat of the Fifth Crusade on the Nile River because they didn’t consider the geography of when the Nile would flood and stop their advance. Another example was how Emperor Frederick II was able to gain more by negotiation than the previous Crusaders had gained by war, because he spoke Arabic and was able to gain their trust.
Jones explains that the Crusades included the “Reconquista,” the seven hundred years of battles for Spain to retake the Iberian Peninsula from the Muslims, which finally ended in 1492. Thus, instead of seeing the Crusades as a total failure, since the Crusaders were expelled from the Holy Land after the fall of Acre in 1291, he sees the battle for Spain as a success for the crusaders. He even cities numerous occasions when crusaders on their way to the Holy Land would stop off in Spain and help them win a battle, then sail on for Jerusalem. The author explains how, even as Europe lost interest in raising large international armies to fight Muslims in the Holy Land, the crusading spirit continued and degenerated into hunting down heretics in southern France, fighting pagan tribes in the Balkans, and even papal battles against Christian rulers who refused to submit to the pope.
I wish that Jones had explained more of the results of the Crusades. He does allude to how it gave power to the pope, and he ends the book by explaining the anti-Christian bitterness that remains among Muslims in the Middle East. He could have said more about how it affected Muslim treatment of Christian minorities in the Middle East, and how the contact opened doors of economic, cultural, and intellectual trade between East and West, even helping bring Arabic numerals and Aristotle’s philosophy to the West.
Sadly, Jones points out that the Crusades never fully ended, as Osama bin Laden referred to President George W. Bush as “the Chief Crusader… under the banner of the cross.” As ISIS leader Abu Bakr al-Baghdadi said, “the battle of Islam and its people against the crusaders and their followers is a long battle.”
My new Miss. Baptist history book is now available!

My new book, Mississippi Baptists: A History of Southern Baptists in the Magnolia State, has been published by the Mississippi Baptist Convention Board, and is now available to the public. It is a hardback book, 300 pages of text, plus four appendices, notes, and an index in the back.
In 2021, I signed a contract with the Mississippi Baptist Convention Board and Mississippi Baptist Historical Commission to revise and update R.A. McLemore’s book published in 1971, A History of Mississippi Baptists. While the new work is based on McLemore’s history, it has many more new features than simply the addition of a half century of recent history. I have included new research from the beginning. For example, I discovered evidence that the mother church of Mississippi Baptists was Ebenezer Baptist Church, Florence, South Carolina. Other new research includes the declaration of religious liberty by Richard Curtis, Jr., the first Baptist pastor in Mississippi; social and cultural information on typical Baptist life during different time periods; trends in Baptist theology; and details of the previously untold story of the McCall controversy of 1948-49. Throughout the book, I sought to write in a narrative style, including anecdotes that reflected the flavor of Baptist life.
You can get a book by making a donation to the Mississippi Baptist Historical Commission at the link below. Click on “Donate to the Historical Commission,” then fill out the form, select “MS Baptist Historical Commission” and how much you will donate (I suggest at least $15 to cover their costs), and how many copies of the book you want.
Here is the link: https://mbcb.org/historicalcommission/
The chaotic 1930 special session of the Miss. Baptist Convention

Copyright by Robert C. Rogers and the Mississippi Baptist Convention Board.
On July 15, 1930, an unprecedented second special session of the Mississippi Baptist Convention met in Newton, attended by 318 messengers. It turned into chaos.
(A first special session had been held in April to respond to the problems of the Great Depression by closing Clarke College and moving the Mississippi Baptist Orphanage to the campus of Clarke; however, some legal matters were not handled, so a second special session was called.)
This second special session erupted into a chaotic state of confusion, described by The Baptist Record as featuring “unanimous disagreement, often vociferously expressed.” MBCB executive R.B. Gunter made a plea for harmony, but it went unheard. W.N. Taylor of Clinton presented resolutions to continue Clarke College and keep the orphanage near Jackson, in effect to rescind the vote of the previous session. Convention president Gates ruled the resolutions out of order, but a challenge was made to his ruling; the messengers voted 164-154 to sustain his ruling. Next, M.P. Love of Hattiesburg moved that the property of the orphanage be mortgaged to pay the debts of Clarke College, but his resolutions were voted down. At a stalemate, the messengers then adjourned to dinner.
The Baptist Record commented that the only thing the messengers agreed about was that “the people of Newton and vicinity furnished a good dinner.” After dinner, the messengers returned and reversed their earlier actions. This time, Gates’ ruling was overturned. Next, the messengers adopted Taylor’s resolutions, voting to keep the orphanage in Jackson and to re-open Clarke College. To pay for it, the messengers authorized the trustees to borrow the money, using the property of the college and orphanage as security. In addition, they pledged an extra $10,000 each to Blue Mountain College and Mississippi Woman’s College. The debacle of these two special sessions taught Mississippi Baptists a lesson they had not learned from the 1892 convention (which attempted to relocate Mississippi College, only to have it overturned later): attempts to operate their institutions from the floor of the convention could lead to great confusion and chaos.
(Dr. Rogers is the author of the new book, Mississippi Baptists: A History of Southern Baptists in the Magnolia State.)
Mississippi Baptists and the civil rights struggle in the 1950s and 1960s
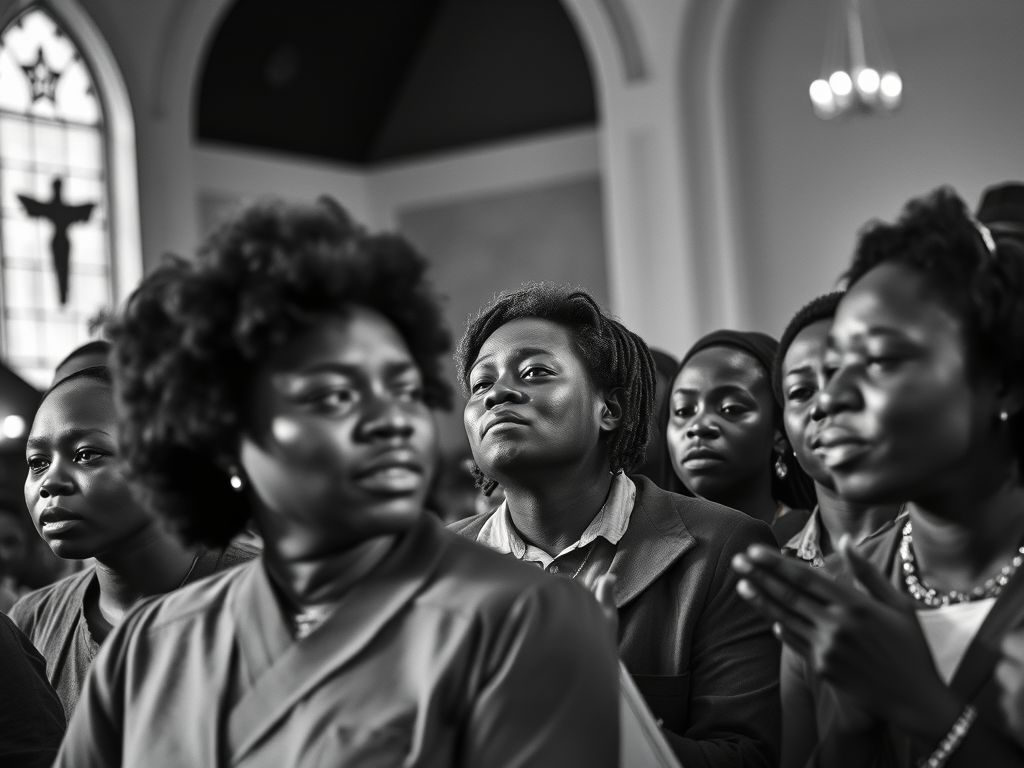
Copyright by Robert C. Rogers and the Mississippi Baptist Convention Board.
On May 17, 1954, the Supreme Court struck down public school segregation in Brown v. Board of Education, saying, “Separate educational facilities are inherently unequal.” The Southern Baptist Convention, meeting only weeks later, became the first major religious denomination to endorse the decision, saying, “This Supreme Court decision is in harmony with the constitutional guarantee of equal freedom to all citizens, and with the Christian principles of equal justice and love for all men.” Mississippi Baptists, however, would have none of it. A.L. Goodrich, editor of The Baptist Record, accused the Southern Baptist Convention of inconsistency on the issue for not endorsing other types of integration as well. Goodrich was “indignant” at this example of “the church putting its finger in state matters,” but he told Mississippi Baptist readers that they “need not fear any results from this action.” First Baptist Church, Grenada (Grenada) made a statement condemning the Supreme Court decision. The Mississippi Baptist Convention, meeting November 16-18, 1954, passed several resolutions, but it made no mention of the Supreme Court decision.1
The Supreme Court deferred application of integration, and Mississippi’s governor, Hugh White, met with Black leaders, expecting that they would agree to maintain segregated schools if the state improved funding for Black schools. H.H. Humes represented the largest Black denomination in the state, as president of the 400,000-member General Missionary Baptist Convention. He responded to the governor, “the real trouble is that for too long you have given us schools in which we could study the earth through the floor and the stars through the roof.”2
In the 1950s, most White Baptists were content with a paternalistic approach of sponsoring ministry to Black Baptists, while keeping their schools, churches and social interaction segregated. There were some rare exceptions. Ken West recalls attending Gunnison Baptist Church, (Bolivar) in the 1950s, when the congregation had several Black members of the church, mostly women, who actively participated in WMU. However, most White Baptists agreed with W. Douglas Hudgins, pastor of First Baptist Church, Jackson (Hinds), who told reporters that he did not expect “Negroes” to try to join his church. When pressed specifically about the Brown v. Board of Education decision of the Supreme Court, Douglas evasively called it “a political question and not a religious question.” Alex McKeigney, a deacon from First Baptist Church, Jackson, was more direct, saying that “the facts of history make it plain that the development of civilization and of Christianity itself has rested in the hands of the white race” and that support of school desegregation “is a direct contribution to the efforts of those groups advocating intermarriage between the races.” Dr. D.M. Nelson, president of Mississippi College, wrote a tract in support of segregation that was published by the White Citizens’ Council in 1954. In the tract, Nelson said that in part, the purpose of integration was “to mongrelize the two dominant races of the South.” Baptist lay leader Owen Cooper recalled that during the 1950s, he avoided the moral issue that troubled him later: “To be quite honest I did not ask myself what Jesus Christ would have done had He been on earth at the time. I didn’t ask because I already knew the answer.”3
In 1960, Baptist home missionary Victor M. Kaneubbe sparked controversy over segregated schools for another racial group in Mississippi, the American Indians. Kaneubbe was a member of the Choctaw Nation of Oklahoma, who came to Mississippi to do mission work with the Mississippi Band of Choctaw Indians. However, since his wife was White, no public schools would admit their daughter, Vicki. The White schools denied Vicki because she was Choctaw, and the Choctaw schools denied her because she was White. Kaneubbe enlisted the support of many White Baptists who campaigned for Vicki. This eventually led to the establishment Choctaw Central High School on the Pearl River Reservation in Neshoba County, an integrated school that admitted students with partial Choctaw blood.4
The minutes of Woodville Heights Baptist Church, Jackson (Hinds) illustrate how local churches began to struggle with the issue of integration in the 1960s. At the monthly business meeting of Woodville Heights in August 1961, the issue of racial integration came up. The minutes read, “Bro. Magee gave a short talk on integration attempts. Bro. Sullivan gave his opinion on this subject. Bro. Sullivan said he would contact Sheriff Gilfoy concerning the furnishing of a Deputy during our services.” Interestingly, the very next month, the pastor, Dr. Percy F. Herring, resigned, and so did one of the trustees, Samuel Norris. In his resignation letter, Herring did not make a direct reference to the integration issue, only saying, “My personal circumstances and the situation here in the community have combined to bring me to the conclusion that I should submit my resignation as Pastor of this church.”5
Woodville Heights was not alone in the struggle. Throughout the 1960s, many Mississippi Baptists wrestled with racism in their local churches, associations, and the state convention. In the early part of the decade, it was common for Southern Baptist churches in Mississippi to have what was called a “closed door policy” against attendance by Black people. White Baptists were known to be active in the Ku Klux Klan, such as Sam Bowers, leader of the White Knights of the KKK, who taught a men’s Sunday school class at a Baptist church in Jones County. Some Baptist leaders were disturbed by the violence of the KKK. In November 1964, a few months after the murders of civil rights workers in Neshoba County, Owen Cooper presented a resolution on racism at the state convention. Cooper’s resolution, which was adopted, recognized that “serious racial problems now beset our state,” and said, “we deplore every action of violence… We would urge all Baptists in the state to refrain from participating in or approval of any such acts of lawlessness.” In 1965, it was front-page news in The Baptist Record when First Baptist Church, Richmond, Virginia admitted two Nigerian college students as members. When First Baptist Church, Montgomery, Alabama adopted an “open door policy” toward all races the same year, it was again news in The Baptist Record. Clearly, it was not yet the norm in White Mississippi Baptist churches.6
As the decade progressed, some Mississippi Baptists began to accept integration and work toward racial justice and reconciliation. Tom Landrum, a Baptist layman in Jones County, secretly spied on the White Knights of the Ku Klux Klan. Landrum’s reports to the Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) were instrumental in the arrest of the Klansmen who killed civil rights leader Vernon Dahmer in 1965. Earl Kelly, in his presidential address in 1966, told the Mississippi Baptist Convention that “the race question” had to be faced. Baptist deacon Owen Cooper took this challenge seriously, helping to charter and becoming chairman of Mississippi Action for Progress (MAP) on September 13, 1966; MAP was able to secure millions of dollars to keep alive Head Start programs, which primarily benefitted impoverished Black children, that were in danger of losing their funds. When civil rights leader Martin Luther King, Jr. was assassinated in 1968, The Baptist Record quoted Baptist leaders who expressed “shock, grief and dismay at the murder” of King. In 1969, Jerry Clower, the popular Mississippi entertainer and member of First Baptist Church, Yazoo City (Yazoo), was speaking out against racism at Baptist events. Clower confessed that as a child, he was taught that “a Negro did not have a soul, but he found out he was wrong when he became a Christian.” By that year, 1969, all the state colleges and hospitals had agreed to sign an assurance of compliance with racial integration.7
(Dr. Rogers is the author of Mississippi Baptists: A History of Southern Baptists in the Magnolia State, to be published in 2025.)
SOURCES:
1 Jesse C. Fletcher, The Southern Baptist Convention: A Sesquicentennial History (Nashville: Broadman and Holman Publishers, 1994), 200; Annual, Southern Baptist Convention, 1954, 36; Minutes, Mississippi Baptist Convention, 1954, 45-49; The Baptist Record, June 10, 1954, 1, 3; July 8, 1954, 4.
3 Ibid, 62-63; Letter from Ken West, Leland, Mississippi, to Bob Rogers, Hattiesburg, Mississippi, 28 January 2022, Original in the hand of Robert C. Rogers; D. M. Nelson, Conflicting Views on Segregation (Greenwood, MS: Educational Fund of the Citizens’ Council, 1954), 5, 10; The Clarion-Ledger, April 4, 1982, cited in Dittmer, 63.
4 Jamie Henton, “Their Culture Against Them: The Assimilation of Native American Children Through Progressive Education, 1930-1960s,” Master’s Theses, University of Southern Mississippi, 2019, 85-92.
5 Minutes, Woodville Heights Baptist Church, Jackson, Mississippi, August 9, 1961; September 6, 1961.
6 Curtis Wilkie, When Evil Lived in Laurel: The ‘White Knights’ and the Murder of Vernon Dahmer (New York: W.W. North & Company, 2021), 26, 43-51; Minutes, Mississippi Baptist Convention, 1964, 43-44; The Baptist Record, January 28, 1965, 1; April 29, 1965, 2.
7 Wilkie, 20, 138; Dittmer, 377-378; The Baptist Record, November 17, 1966, 1, 3; December 21, 1967; April 11, 1968, 1; July 17, 1969, 1, 2; November 29, 1969, 1.
A challenge to Calvinism: M.T. Martin and the controversy that rocked Mississippi Baptists in the 1890s
Copyright by Robert C. Rogers and the Mississippi Baptist Convention Board.
In 1893, a controversy began in the Mississippi Baptist Association and eventually spread across the state. Jesse Boyd wrote, “Its rise was gradual, its force cumulative, its aftermath bitter, and its resultant breach slow in healing.”1 While it may have been a quibble over words rather than a serious breach of Baptist doctrine, it illustrates how Mississippi Baptists clashed over Calvinist doctrine by the end of the 19th century.
M. Thomas Martin was professor of mathematics at Mississippi College from 1871-80, and he also served as the business manager of The Baptist Record from 1877-81. He moved to Texas in 1883, where he had great success as an evangelist for nearly a decade, reporting some 4,000 professions of faith. However, his methods of evangelism drew critics in Texas. According to J.H. Lane, while Martin was still in Texas, “the church in Waco, Texas, of which Dr. B. H. Carroll is pastor, tried Bro. Martin some years ago, and found him way out of line, for which he was deposed from the ministry.” In 1892 Martin returned to Mississippi and became pastor of Galilee Baptist Church, Gloster (Amite). Martin preached the annual sermon at the Mississippi association in 1893. His sermon had such an effect on those present, that the clerk entered in the minutes, “Immediately after the sermon, forty persons came forward and said that they had peace with God, and full assurance for the first time.” The following year, Mississippi association reported on Martin’s mission work in reviving four churches, during which he baptized 19 people, and another 60 in his own pastorate. Soon Mississippi Baptists echoed the Texas critics that he was “way out of line,” not because he baptized so many, but because so many were “rebaptisms.”2
The crux of the controversy was Martin’s emphasis on “full assurance,” which often led people who had previously professed faith and been baptized, to question their salvation and seek baptism again. In 1895, the Mississippi association called Martin’s teachings “heresy” and censured Martin and Galilee for practicing rebaptism “to an unlimited extent, unwarranted by Scriptures.” When the association met again in 1896, resolutions were presented against Galilee for not taking action against their pastor, but other representatives said they had no authority to meddle in matters of local church autonomy. As a compromise, the association passed a resolution requesting that The Baptist Record publish articles by Martin explaining his views, alongside articles by the association opposing those views, “that our denomination may be… enabled to judge whether his teachings be orthodox or not.” The editor of The Baptist Record honored the request, and Martin’s views appeared in the paper the following year. The association enlisted R.A. Venable to write against him, but Venable declined to do so. Martin also published a pamphlet entitled The Doctrinal Views of M.T. Martin. When these two publications appeared, what had been little more than a dust devil of controversy in one association, developed into a hurricane encompassing the entire state.3
Most of Martin’s teachings on salvation were common among Baptists. Even his opponent, J.H. Lane, admitted, “Some of Bro. Martin’s doctrine is sound.” Martin taught that the Holy Spirit causes people to be aware that they are lost, and the Spirit enables people to repent and believe in Christ. He taught that people are saved by grace alone, through faith, rather than works, and when people are saved, they should be baptized as an act of Christian obedience. Martin said that salvation does not depend on one’s feelings, and that children of God have no reason to question their assurance of salvation.
These teachings were not controversial. What was controversial, however, was what Lane called “doctrine that is not Baptist,” and what T.C. Schilling said “is not in accord with Baptists.” Martin said if a man doubted his Christian experience, then he was never true a believer.
He considered such doubt to be evidence that one’s spiritual experience was not genuine, and the person needed to be baptized again. “If you have trusted the Lord Jesus Christ,” Martin would say, “you will be the first one to know it, and the last one to give it up.” He frequently said, “We do wrong to comfort those who doubt their salvation, because we seek to comfort those whom the Lord has not comforted.” Therefore, Martin called for people who questioned their salvation to receive baptism regardless of whether they had been baptized before. “I believe in real believer’s baptism, and I do not believe that one is a believer until he has discarded all self-righteousness, and has looked to Christ as his only hope forever… I believe that every case of re-baptism should stand on its own merits, and be left with the pastor and the church.”4
The 1897 session of the Mississippi association took further action against Martinism. They withdrew fellowship from Zion Hill Baptist Church (Amite) for endorsing Martin and urged Baptists not “to recognize him as a Baptist minister.” The association urged churches under the influence of Martinism to return to the “old faith of Baptists,” and if not, they would forfeit membership. When the state convention met in 1897, some wanted to leave the issue alone, but others forced it. The convention voted to appoint a committee to report “upon the subject of ‘Martinism.’” Following their report, the convention adopted a resolution of censure by a vote of 101-16, saying, “Resolved, That this Convention does not endorse, but condemns, the doctrinal views of Prof. M. T. Martin.” While a strong majority condemned Martinism, a significant minority of Baptists in the state disagreed. From 1895 to 1900, the Mississippi association declined from 31 to 22 churches, and from 3,042 to 2,208 members. In 1905, the state convention adopted a resolution expressing regret for the censure of Martin in 1897.5
Earl Kelly observed two interesting doctrinal facts that the controversy over Martinism revealed about Mississippi Baptists during this period: “First, the Augustinian conception of grace was held by the majority of Mississippi Baptists; and second, Arminianism was beginning to make serious inroads into the previously Calvinistic theology of these Baptists.” It is significant that Mississippi association referred to Martinism as a rejection of “the old faith of Baptists,” and that when J.R. Sample defended Martin, Lane pointed out that Sample was formerly a Methodist.6
(Dr. Rogers is the author of Mississippi Baptists: A History of Southern Baptists in the Magnolia State, to be published in 2025.)
SOURCES:
1 Jesse L. Boyd, A Popular History of the Baptists of Mississippi (Jackson: The Baptist Press, 1930), 178-179.
2 Boyd, 196-197; Minutes, Mississippi Baptist Association, 1893; 7; Z. T Leavell and T. J. Bailey, A Complete History of Mississippi Baptists from the Earliest Times, vol. 1 (Jackson: Mississippi Baptist Publishing Company, 1904), 68-69; The Baptist Record, May 6, 1897.
3 Minutes, Mississippi Baptist Association, 1895; 1896, 9.
4 Boyd, 179-180; The Baptist Record, March 18, 1897, May 6, 1897, June 24, 1897, 2.
5 Minutes, Mississippi Baptist Association, 1897, 6, 14; Minutes, Mississippi Baptist Convention, 1897, 13, 17, 18, 22, 31; 1905, 47-48; Leavell and Bailey, vol. 1, 70; Boyd, 198. Martin died of a heart attack while riding a train in Louisiana in 1898, and he was buried in Gloster.
6 Earnest Earl Kelly, “A History of the Mississippi Baptist Convention from Its Conception to 1900.” (Unpublished Doctoral Thesis, Southern Baptist Theological Seminary, Lousville, Kentucky, 1953), 114; The Baptist Record, May 6, 1897.
Natchez to New Orleans: How those “country Baptists” of Mississippi sought to reach the cities in the antebellum era

Copyright by Robert C. Rogers and the Mississippi Baptist Convention Board.
Although Mississippi had grown to a population of nearly 800,000 by the Civil War, the vast majority lived in rural areas. Like the citizens, Mississippi Baptist churches were more often in rural settlements than towns, and few were on the Gulf Coast. Pearl River Baptist Association only had one church in a coastal county, Red Creek Baptist Church (Harrison), and Red Creek was a rural area inland from the coast. By 1860, though, several towns in Mississippi had over 1,000 residents: Natchez was the largest, with 6,619 residents, followed by Vicksburg with 4,591, Columbus with 3,308, Jackson with 3,199, Holly Springs with 2,987, and Port Gibson with 1,453. Clinton, home of Mississippi College, had 289 citizens.1
Although the Columbus Baptist Church, Columbus (Lowndes) was thriving, the Mississippi Baptist Convention recognized the need to plant churches in many of the other emerging cities and towns. In 1848, the convention gave $100 each to pastors in Yazoo City, Jackson, Vicksburg and Grenada. That year, S.I. Caldwell, pastor of First Baptist Church, Jackson (Hinds), reported the house of worship had been completed and that the membership had increased by 15 White members and 11 Black members. In 1853, I.T. Hinton, in the report of the Southern Baptist Domestic Mission Board, pointed out the need for placing missionaries in the state capital and the chief commercial towns, including Jackson, Vicksburg, Natchez, Biloxi and the Gulf Coast, all of which received aid. The Domestic Mission Board reported that the minister of the “church in Jackson, the capital received a commission from this Board. A large revival of religion has added very greatly to the strength of the church, however, rendering our aid unnecessary.”2
Natchez Baptist Church, Natchez (Adams) was restarted by Ashley Vaughn in 1837 and began to prosper under the pastorate of W.H. Anderson in the 1840s, but they were never able to build a meeting place of their own. They met at a Presbyterian church, at the courthouse, and at the Natchez Institute. In 1848, they called Rev. T.G. Freeman as pastor, but the church underwent a bitter split in 1849, and Freeman led in the formation of a new Baptist congregation, Wall Street Baptist, Natchez (Adams) in April 1850. The new congregation moved rapidly to build a sanctuary, breaking ground a month later at the corner of Wall Street and State Street, across from the Adams County Courthouse. They reported to the 1852 meeting of the Central Baptist Association that they had “erected a house of worship at a cost of $7,000 and paid for—the first ever owned by the Baptists in this city.” That year, Wall Street had 41 White members and three Black members, while Natchez Baptist Church had 34 White members and 412 Black members. Three years later, Wall Street had grown to 131 White and 105 Black members and held services four Sundays a month. Wall Street continued to grow, and proudly hosted the 1860 Mississippi Baptist Convention, whereas Natchez Baptist Church dissolved in 1857; its Black members were absorbed into Rose Hill Baptist Church, Natchez (Adams) an independent Black congregation that met on Madison Street. In 1918, Wall Street Baptist Church adopted the name First Baptist Church, Natchez, which remains to this day.3
By 1859, several town churches reported strong membership numbers to the state convention, including First Baptist Church, Jackson (Hinds) with 309 members, Canton Baptist Church, Canton (Madison) with 197 members, and Vicksburg Baptist Church, Vicksburg (Warren) with 160 members. An indirect result of the Baptists taking control of Mississippi College in 1850 was that a Baptist church was developed in Clinton. In the nine years afterward, Clinton Baptist Church, Clinton (Hinds) became the second largest of the five churches in the town. In May 1860, W. Jordan Denson described the church this way: “At present the Baptist Church of Clinton is enjoying one of those powerful revivals of religion, that she has so frequently been blessed with since the location of the college in that village. Last Sunday twenty-two were baptized, a large part students. Others will be baptized in two weeks—many others, we have reason to hope.”4
Although outside of the state, Mississippi Baptists took a special interest in reaching the city of New Orleans. The earliest Baptist churches in Louisiana were started by ministers from Mississippi, and those churches were affiliated with associations in Mississippi. New Orleans was an international port and was important to the entire Mississippi River Valley. In 1843, First Baptist Church, New Orleans was organized there with 10 members. It had great difficulty maintaining itself until Isaac T. Hinton became pastor. Under his leadership, the church made remarkable progress, increasing its membership from 27 to 122 members. A yellow fever epidemic in 1847 took the life of the pastor and many members, after which the church declined rapidly, and in 1851 the congregation lost its building to its creditors. The Mississippi Baptist Convention was distressed at this news and adopted resolutions urging the Southern Baptist Convention to help raise funds for a new church building in New Orleans. Several members of the convention made donations or pledges for this project. Finally, in 1861, First Baptist Church, New Orleans had another sanctuary.5
Dr. Rogers is the author of Mississippi Baptists: A History of Southern Baptists in the Magnolia State, to be published in 2025.
SOURCES:
1 Minutes, Pearl River Baptist Association, 1860; U.S. Census, “Population of the United States in 1860: Mississippi,” accessed on the Internet 30 April 2022 at https://www2.census.gov/library/publications/decennial/1860/population/1860a-22.pdf.
2 Minutes, Mississippi Baptist Convention, 1848, 13.
3 Robert C. Rogers, “From Alienation to Integration: A Social History of Baptists in Antebellum Natchez, Mississippi” (Th.D. diss.,, New Orleans Baptist Theological Seminary, 1990), 53-59.
4 Minutes, Mississippi Baptist Convention, 1859, 14-15; 1860, 37.
5 Glen Lee Greene, House Upon a Rock: About Southern Baptists in Louisiana (Alexandria, LA: Executive Board of the Louisiana Baptist Convention, 1973), 41-51, 81-84; Minutes, Mississippi Baptist Convention, 1852, 31; Baptist Record, June 5, 1969.
Preaching to the spirits in prison. An interpretation of 1 Peter 3:18-20
Copyright by Bob Rogers, Th.D.

For Christ also suffered for sins once for all, the righteous for the unrighteous, that He might bring you to God, after being put to death in the fleshly realm but made alive in the spiritual realm. In that state He also went and made a proclamation to the spirits in prison who in the past were disobedient, when God patiently waited in the days of Noah while an ark was being prepared. – 1 Peter 3:18-20, HCSB
There are three facts about 1 Peter 3:18-20 which cannot be ignored:
- There was a story in a Jewish book called First Enoch about Enoch (Genesis 5:21-24) who made a journey to the supernatural beings who seduced human women (Genesis 6:1-4). This was at the time of Noah (Genesis 6:5-8). In First Enoch, Enoch is said to preach condemnation on these beings.
- First Enoch was well known in the first century, for Jude 9-10 and Jude 14 and 2 Peter 2:4-5 refer to stories which are in the older book of First Enoch, as does this passage.
- In Greek, verse 19 begins with three words which are transliterated in English letters: en o kai, which in Greek manuscripts would be run together: enokai. Compare that to the name Enoch.
What does all this mean? 1 Peter is well-known for clever arrangements of words. It seems that he is making a pun on the name Enoch in verse 19 because he is referring to a story about Enoch known to his readers.
First Peter 3:18 says that after Jesus died and was buried, he was “made alive in the spiritual realm.” Yet before His resurrection was physically displayed on Easter, He took care of some other-worldly business. He made a journey to the lower world of the dead (see Romans 10:7, Ephesians 4:9), where He “made a proclamation to the spirits in prison” (verse 19). The term “spirits” is never used to mean dead men, so it must refer to the fallen angels of Noah’s day, whom God had bound in prison (Jude 6, 1 Peter 2:4, Revelation 20:1-2, First Enoch 10).
Nowhere does Peter say that Jesus went to hell as punishment for our sins. The journey was to “Tartarus” (2 Peter 2:4, incorrectly translated “hell” in some translations). Tartarus was a Greek name for a place they believed all dead went, good and bad, like Hebrew word Sheol in the Old Testament. This journey was not forced upon Jesus; He went rather than suffer agony while in the grave.
Peter’s readers lived in a world where belief in evil spirits was universal. Some saw the Roman persecution coming, and they longed for protection from the evil spirits of the Romans which they feared might overcome the power of Christ. Peter comforted them with the news that Christ had defeated the most horrible of all spirits, the greatly feared fallen spirits of Noah’s day. In folklore, these spirits were considered to be the most wicked of all spirits.
First Peter 3:19 says Christ made proclamation to these spirits. This does not mean He was giving those who died before the time of His crucifixion a chance to believe the gospel, for he was speaking to spirits, not men. It does not even mean he was presenting the gospel to the spirits, for this Greek word can be used simply to “declare” or “proclaim” (the translation used in many versions, see also Revelation 5:2) with no implication of the gospel being presented. No, Jesus was announcing that He had defeated them! Thus, in verse 22, Peter says He ascended to heaven “with angels, authorities, and powers subject to Him.”
This proclamation of victory over the fallen angels was reassurance to Peter’s readers that they shouldn’t fear evil powers around them, for Christ is more powerful.
A second interpretation of 1 Peter 3:18-20 is worth considering. This view says that Jesus did not descend at all, but that in the same spirit of Jesus which has always existed, He had preached to the evil men of Noah’s day and given them a chance to repent. This takes verse 19 to refer to “in the spiritual realm” in verse 18.
This view appears to answer some questions people have, because it claims that the people living before the time of Jesus’ crucifixion had the same opportunity to repent as we do, for the spirit of Christ has always been around to give them the message, whether it be seen in Noah or Moses or a prophet.
This view is correct in noting that verse 19 simply says, “He went,” not “He descended.” It is also less complicated than the other view.
However, this second explanation seems to take things out of order. In verse 18, Peter refers to the cross, and in verse 22, he refers to the ascension. Verses 19-20 should refer to something in between, not to Jesus’ spirit back in the days of Noah.
Whatever interpretation we+9 follow, we would do well to remember to present it in “gentleness and respect” (1 Peter 3:15).
Further reading: Ernest Best, 1 Peter in the New Century Bible Commentary Series (Grand Rapids, MI: Eerdmans, 1971), 135-146.
E.G. Selwyn, The First Epistle of St. Peter, 2nd ed. (Grand Rapids, MI: Baker Book House, 1946), 197-202.
Ray Summers, “1 Peter” in volume 12 of The Broadman Bible Commentary (Nashville: Broadman Press, 1972), 163-164.
How Mississippi Baptist views on alcohol evolved in the 19th century

Copyright by Robert C. Rogers and the Mississippi Baptist Convention Board.
During the 1820s and 1830s, Baptists gradually took a stronger stand against liquor. In 1820, Providence Baptist Church (Forrest County) discussed the question, “Is it lawful, according to scripture, for a member of a church to retail spiritous liquors?” The church could not agree on a position. However, in 1826, the influential Congregationalist pastor Lyman Beecher began a series of sermons against the dangers of drunkenness. He called on Christians to sign pledges to abstain from alcohol, igniting the temperance movement in America. The question came before the Mississippi association in 1827, and the association stated that it “considers drunkenness one of the most injurious and worst vices in the community.” In 1830, the Pearl River association admonished any churches hosting their meetings, “Provide no ardent spirits for the association when she may hereafter meet, as we do not want it.” In 1831, Pearl River association thanked the host church for obeying their request, and in 1832, the association humbly prayed for “the public, that they will not come up to our Association with their beer, Cider, Cakes, and Mellons, as they greatly disturb the congregation.” Likewise in 1832, the Mississippi association resolved, “that this Association do discountenance all traffic in spirituous liquors, beer, cider, or bread, within such a distance of our meetings as in any wise disturb our peace and worship; and we do, therefore, earnestly request all persons to refrain from the same.”
It had always been common to discipline members for drunkenness, but as the temperance movement grew in America, Mississippi Baptists moved gradually from a policy of tolerating mild use of alcohol, toward a policy of complete abstinence. A Committee on Temperance made an enthusiastic report in 1838 of “the steady progress of the Temperance Reformation in different parts of Mississippi and Louisiana; prejudices and opposition are fast melting away.” In 1839, D. B. Crawford gave a report to the convention on temperance which stated, “That notwithstanding, a few years since, the greater portion of our beloved and fast growing state, was under the influence of the habitual use of that liquid fire, which in its nature is so well calculated to ruin the fortunes, the lives and the souls of men, and spread devastation and ruin over the whole of our land; yet we rejoice to learn, that the cause of temperance is steadily advancing in the different parts of our State… We do therefore most earnestly and affectionately recommend to the members of our churches… to carry on and advance the great cause of temperance: 1. By abstaining entirely from the habitual use of all intoxicating liquors. 2. By using all the influence they may have, to unite others in this good work of advancing the noble enterprise contemplated by the friends of temperance.” Local churches consistently disciplined members for drunkenness, but they were slower to oppose the sale or use of alcohol. For example, in May 1844, “a query was proposed” at Providence Baptist Church (Forrest) on the issue of distributing alcohol. After discussion, the church took a vote on its opposition to “members of this church retailing or trafficking in Spirituous Liquors.” In the church minutes, the clerk wrote that the motion “unanimously carried in opposition” but then crossed out the word “unanimously.” In January 1845, Providence voted that “the voice of the church be taken to reconsider” the matter of liquor. The motion passed, but then they tabled the issue, and it did not come back up. In March of that year, a member acknowledged his “excessive use of arden[t] spirits” and his acknowledgement was accepted; he was “exonerated.”
By the 1850s, the state convention was calling not only for abstinence, but for legal action as well. In 1853, the convention adopted the report of the Temperance Committee that said, “The time has arrived when the only true policy for the advocates of Temperance to pursue, is… to secure the enactment by the Legislature of a law, utterly prohibiting the sale of ardent spirits in any quantities whatsoever.” They endorsed the enactment of the Maine Liquor Law in Mississippi. In 1851, Maine had become the first state to pass a prohibition of alcohol “except for mechanical, medicinal and manufacturing purposes,” and this law was hotly debated all over the nation, as other states considered adopting similar laws. In 1854, the Mississippi legislature banned the sale of liquors “in any quantity whatever, within five miles of said college,” referring to Mississippi College. In 1855, Ebenezer Baptist Church (Amite) granted permission to the ”sons of temperance” to build a “temperance hall” on land belonging to the church. In 1860, a member of Bethesda Baptist Church (Hinds) confessed he “had been selling ardent spirits by the gallon” and “acknowledged he had done wrong and would do so no more.” He was “requested by the church not to treat his friends with spiritous [sic] liquors when visiting his house.”
Frances E. Willard, one of the most famous temperance activists in the nation, spent a month in Mississippi in 1882 and announced, “Mississippi is the strongest of the Southern State W.C.T.U. organizations.” Every Baptist association had a temperance committee. T.J. Bailey, a Baptist minister, was the superintendent of the Anti-Saloon League. Prohibition of alcohol was such an emotionally charged issue that a liquor supporter assassinated Roderic D. Gambrell, son of Mississippi Baptist leader J.B. Gambrell and the editor of a temperance newspaper, The Sword and Shield. Nevertheless, the temperance movement was so successful that by 1897, all but five counties in Mississippi had outlawed the sale of liquor.
Prayer for New Orleans
Copyright by Bob Rogers

Lord, our hearts break for the lives lost in the terrorist attack in New Orleans, and for the injured, traumatized, and their families. It’s a new year, but the old evil rears its ugly head once again. We need Your strength, Lord. Show us how we can provide comfort and help to the hurting, stand strong against injustice, and find courage to refuse to live in fear.

